What is Data Lifecycle Management?
From creation and storage to sharing and deletion, data lifecycle management (DLM) offers a framework for managing data effectively through out its life. Dedicated products automate each stage required by a DLM framework, helping business keep data secure, accurate and available 365 days a year.
What data lifecycle management means
With huge volumes of data being created by enterprise, a robust framework is crucial for managing each and every data point. DLM meaning data lifecycle management introduces best practises for every phase of a data set’s lifecycle including production, cleansing, processing, management, protection, governance, and deletion.
Fully customisable to the enterprise’s specific data lifecycle requirements, DLM frameworks are essential in an era where data floods in from multiple sources including points of sale, social media, and more. Data lifecycle management ensures any business can constantly rely on accurate, reliable and available data at every stage. This data management life cycle helps you make more informed business decisions, identify opportunities for growth, and protect vital data – and brand reputations – from bad actors.
What the 3 main goals of data lifecycle management?
Adopting a comprehensive approach to data helps achieve three goals crucial to any business moving forward:
Delivering security
Guaranteeing availability
Ensure that only authorised personnel can access data as and when they need it while also putting in restrictions to block any unauthorised actions that could damage business continuity and data protection rules.
Ensuring integrity
Data evolves through out its lifecycle, in turn introducing the risk of stakeholders working with outdated and disparate data sets. Effective data lifecycle management ensures that a business only ever utilises the latest, most accurate data sets so all personnel are working with the right data all of the time.
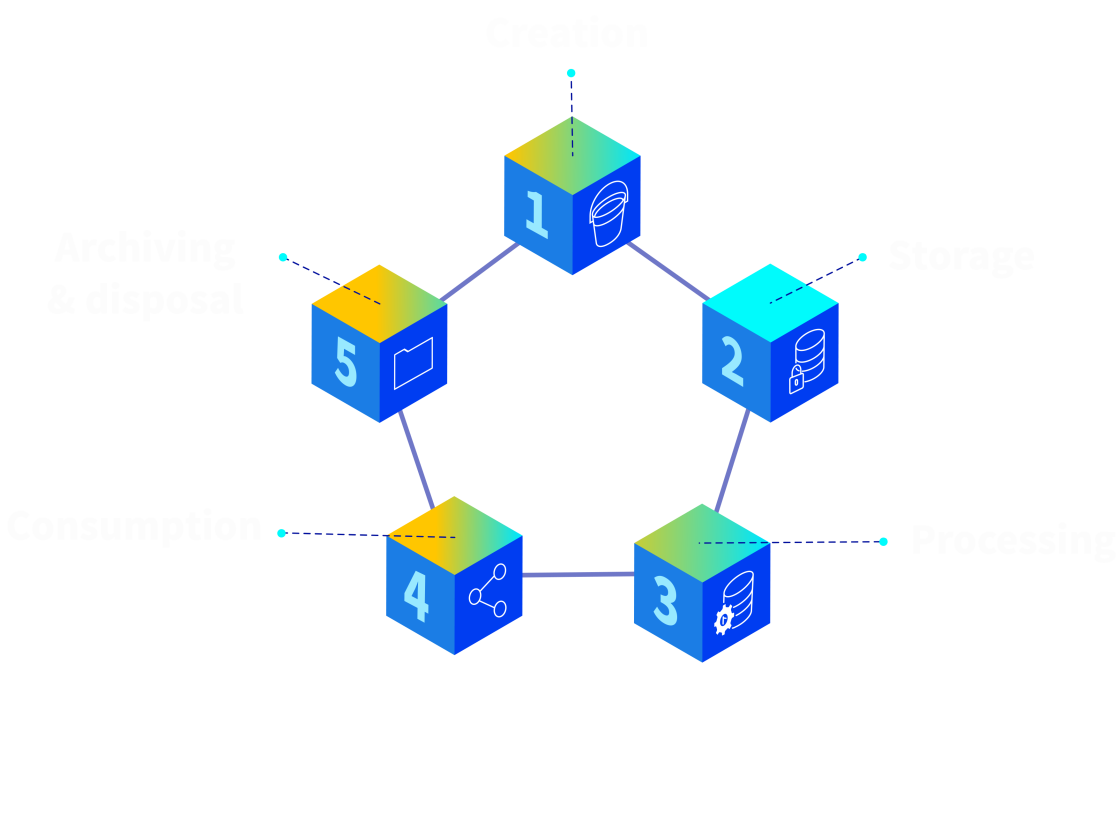
What are the 5 stages of data lifecycle management?
To bring DLM meaning to your lifecycle management, there are typically five key stages that cover your data’s journey from creation to deletion. Here’s how they break down:
1. Data processing
Data is everywhere. Think applications, data entry, social media, surveys, IoT and more. At this stage of data lifecycle management, enterprise decides which data sources should be onboarded and what should be discarded. The data from the finalised sources is gathered in standardised formats – as well as metadata – depending on data type so it is ready for correct storage, management and usage.
To guarantee the integrity of a data management life cycle, all data is fully vetted and cleansed to ensure only accurate, up-to-date information is used. One of the key data security lifecycle phases, policies and rules are now assigned. Is the data to be made available to employees (general internal data) or only specific departments or partners (potentially sensitive data)? Considering data privacy at this early stage of data lifecycle management is also crucial because any personal data storage and usage must meet existing regulatory requirements.
2. Data storage
The data is migrated into the cloud or a new environment for storage. Structured data (such as names, dates and addresses) is typically stored in SQL-driven relational databases. Meanwhile, unstructured data (such as social media posts, videos and audio) is housed in NoSQL or non-relational databases.
Each data set is fully indexed to ensure solutions including CRMs or ERPs can ‘understand’ how to process the inputted data as well as present it correctly through out the data management life cycle. No matter the type of data, its security vulnerabilities are ascertained now before being utilised. Systems are also introduced that provide data backup and recovery options if any data is hacked, breached or corrupted.
3. Data usage
4. Data archiving
Data reaches a point where it is no longer of further daily use in the data analysis lifecycle. An effective data lifecycle management approach recommends that this data is archived securely for the longterm – via a ‘cold archive’ – but kept in case it is required for reporting, compliance, auditing or other purpose at a later stage. As part of a successful data management life cycle, parameters are also set for the archiving process to define where and how long archived data should be kept before being destroyed.
5. Data deletion
The data reaches the end of the data management lifecycle, and is now taking up storage space that could assigned to new data streams. The archived data can now be deleted permanently. As with creating and ingesting data, any data marked for deletion must be destroyed securely, ensuring all regulatory requirements surrounding data protection are still met. This is one of the most important data security lifecycle phases.
OVHcloud and Data Lifecycle Management
We offer several data-focused solutions designed to help you implement and maintain your data lifecycle management framework. From cold archiving services to scalable storage that can house large data sets, OVHcloud helps you keep your data updated, accessible and secure.
*S3 is a registered trademark of Amazon Technologies, Inc. OVHcloud services are not sponsored or approved by, nor affiliated with Amazon Technologies, Inc. in any way.